Artificial Intelligence (AI in short) is a trending technology in the commercial sector, particularly regarding chatbots. One of the objectives of project ENGAGE is to identify how innovative social media technologies, with a significant focus on AI, can contribute to societal resilience. To promote this objective, we highlighted several vital issues that should be considered in adapting such technologies to the field of emergencies, disasters, and societal resilience and the delicate relationship of authorities and first responders with AI technologies.
What is AI?
In short, the term artificial intelligence, or AI, was developed in computer sciences to describe human-like intelligence and capabilities exhibited by machines, either software or hardware (robots), or the simulation of human intelligence in machines. According to IBM, “artificial intelligence enables computers and machines to mimic the perception, learning, problem-solving, and decision-making capabilities of the human mind”. In other words, artificial intelligence is the process of training machines to understand and respond to requests, identify, and learn languages, recognise objects, and improve their decision-making process by learning from examples, sometimes based on trial and error. For example, the ability of a search engine to “translate” a textual query to an image or a video is based on AI, and so does the ability of AI-enabled chatbots to converse with human beings.
Video: Examples of AI capabilities
AI can be considered as a “brain”. Furthermore, as with every brain, some learning is necessary. The learning process that allows AI to get more sophisticated is called Machine Learning (ML in short). ML is the process that gives the technological systems the ability to learn from experiences and data, improve themselves and solve problems without explicitly programming them. In other words, it allows the machine to teach itself, using already existing datasets for training or learning from new data.
AI technologies for emergencies: social media listening and chatbots
The progress of AI technologies is swift and exponential – two generations of progress in every year! Therefore, any relevant suggestion or development while writing these lines might be less relevant a few months later, whilst introducing new and advanced technologies. This also applies to possible limitations, as will be discussed further in this post.
We highlighted several technologies that can be implemented in building societal resilience. For example, social media listening, using AI capabilities to monitor social media channels for tags, mentions, topics and specific keywords. Social media listening allows authorities and first responders to identify very fast-rising and dominant themes in social media.
Why is it important? Think about the following scenarios. First, let us consider that an environmental disaster has started. For example, the water in many areas has changed its taste as an early sign of large-scale pollution, but the relevant measures are still considered normal. So one of the first things that the public might do is to start conversing about these changes in social media. Social media listening allows authorities and first responders to track in real-time that this is a trending topic in social media – that might deserve attention and a rapid response before the measures become poisonous.
The second scenario is related to the fields of misinformation, disinformation and fake news. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many people refused to uptake the vaccine or other medical treatments based on false information they consumed on the internet. However, authorities and first responders worldwide were late to track these chains of false information on time and thus did not respond expediently. Social media listening can identify and alert when a new topic is trending, allowing authorities and first responders to examine whether it is false information that can harm the public – and then respond to it in a timely manner.
Furthermore, social media listening can also support feedback to campaigns and messages developed by authorities and first responders. It allows to track the responses to specific messages, enabling emergency organisations to understand how their message worked (or did not work) and apply the necessary changes.
Video: social media listening
Authorities and first responders raise suspicion
Another important technology that has been the focus of the ENGAGE project to date is AI-enabled chatbots. AI-enabled chatbots allow users to interact with an application that uses AI for communication, text and/or voice-based. AI-enabled chatbots are widely used in customer service, healthcare, and policymaking, accessible via various platforms, such as messaging platforms, social media, websites, and independent platforms. One of their advantages is their ability to support omnichannel communication, allowing the users to connect to it on various platforms.
However, while AI-enabled chatbots are trending globally in the commercial market, the field still lags concerning disaster management and societal resilience. One of our findings in the project is that many authorities and first responders still have high suspicion towards the use of chatbots during emergency management. Some of these concerns are derived from the responsibilities of the authorities and first responders themselves, while others relate to their perceptions of how the users (i.e. the public) will respond to interacting with chatbots during emergencies.
These findings showed that while AI technology may highly contribute to emergency management and societal resilience, much work is still needed to prepare the field for their integration as an intrinsic component of the response to any adversity.
The chatbot
In the ENGAGE project, we developed a blueprint of an AI-enabled chatbot to converse with the public before, during, and after emergencies and disasters. In addition, we suggested how future chatbots can harness cutting-edge, state-of-the-art technologies for collecting and providing information to the public about disasters, augmenting some of the first responders’ roles in communicating with the public.
The suggested blueprint for the chatbot
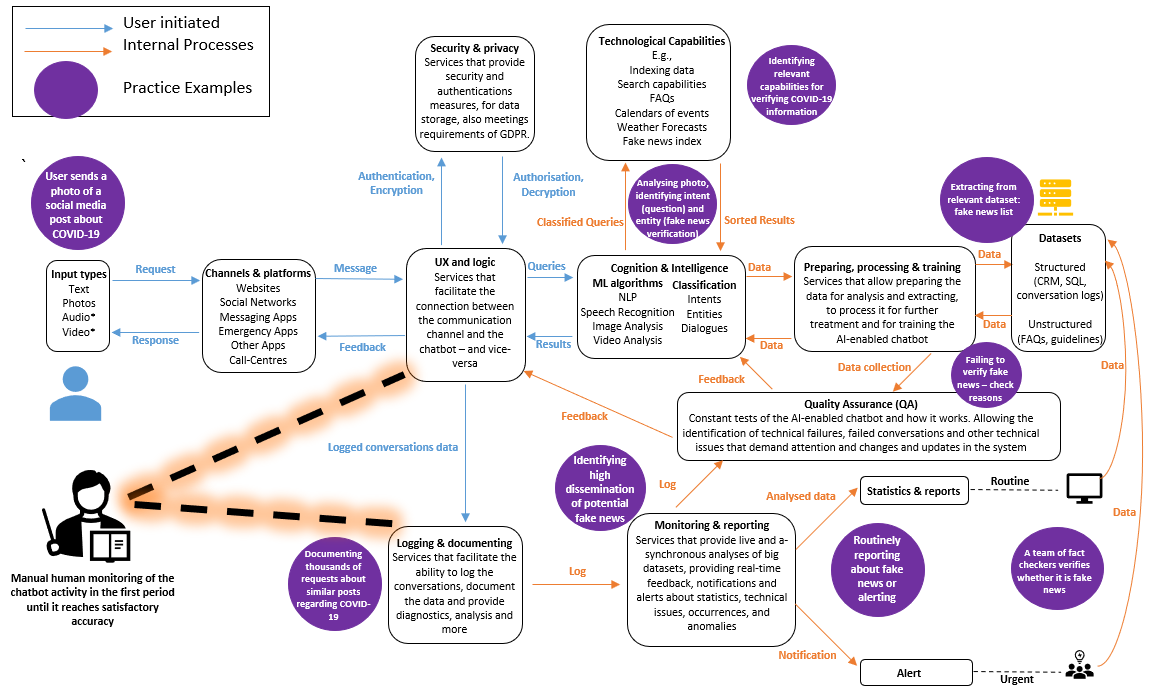
The blueprint reviews the current state-of-the-art technologies and then suggests how and where they can be implemented in the chatbot.
Future directions
Later in the project, we intend to investigate the suggested blueprint further, considering the response of authorities and first responders, along with AI experts and the public. In addition, we wish to further integrate other social media innovative technologies, such as social media listening, as part of innovative solutions for building societal resilience.
View also our Deliverable 3.2 – Exploration of innovative use of communication and social media technologies
Authors: Nathan Stolero, Tomer Simon, Bruria Adini, Kobi Peleg and Moran Bodas (Tel Aviv University, Israel)





